Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Dosha Pitta ↑, Kapha ↓
Subtle Causes of Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Tej
Guna Hetu | Attribute Causes
- Tikshna
- Ushna
Rasa Hetu | Taste Causes
- Amla
- Lavana
- Katu
Imbalance of Dosha, Dhatu, Mala in Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Pitta ↑, Kapha ↓
Dhatu
- Rakta
- Mamsa
Mala
- Mala
Imbalance of Agni, Systems, Organs in Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Rakta Dhatvagni Mandhya
Srotas | Systems
- Rakta
Organs
- Jihva
- Mukha
Vyadhi mode of Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
Apatarpan
RAJVIDYA uploaded new photos
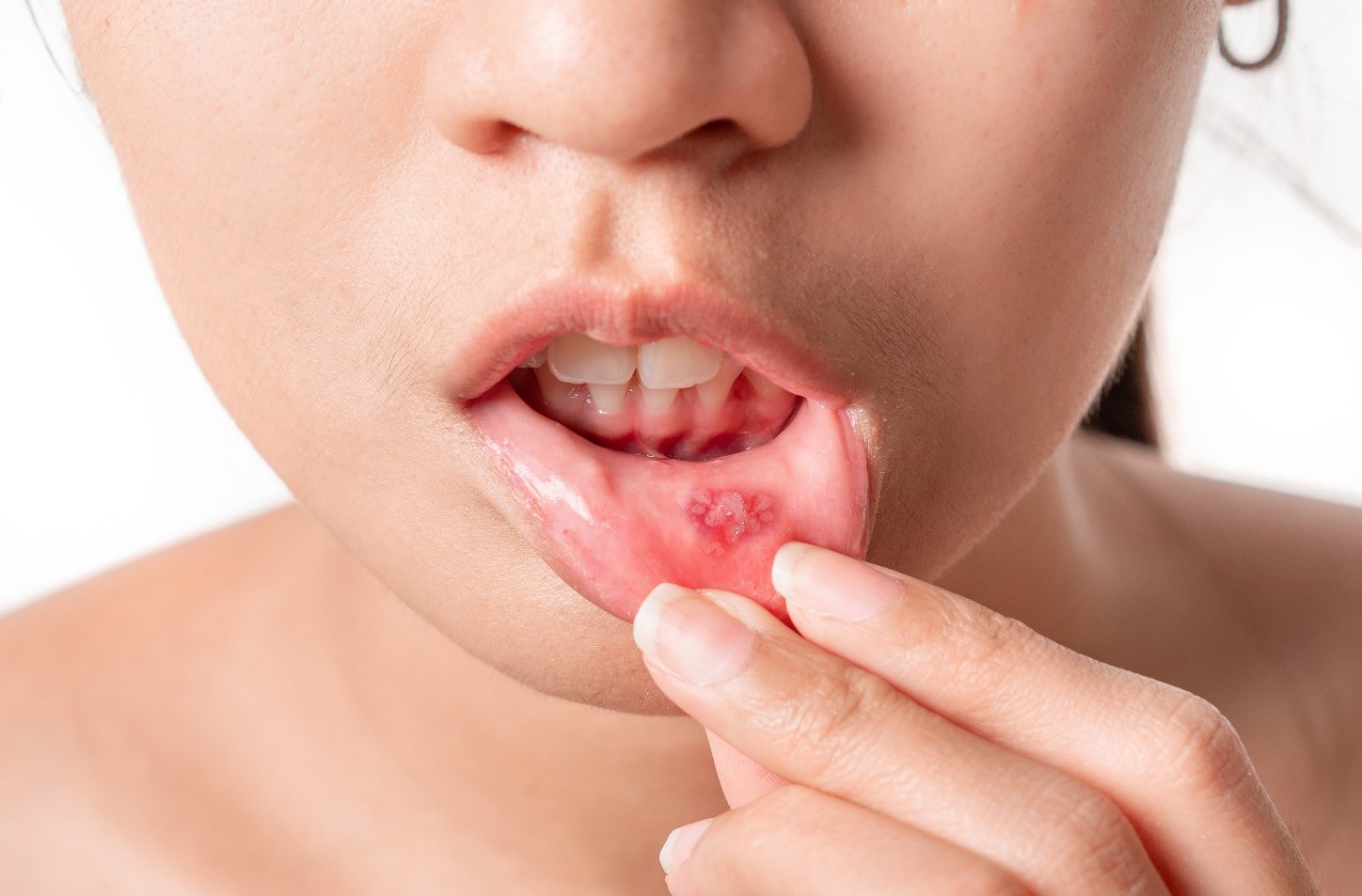
Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka) Defination
Mukha Paaka, or stomatitis, is an inflammatory condition of the mouth characterized by painful sores or ulcers on the inner cheeks, tongue, lips, or gums. In Ayurveda, Mukha Paaka is primarily considered a result of imbalances in Pitta and Kapha doshas, affecting the oral cavity and digestion.
Reference:
- Charaka Samhita, Chikitsa Sthana, 26/34: "Pitta vriddhihi mukha paka hetuh" (The imbalance in Pitta is a primary cause of Mukha Paaka).
Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka) Description
Mukha Paaka, commonly known as stomatitis or mouth ulcers, occurs due to various dietary and lifestyle factors that aggravate Pitta and weaken the body's defenses. It manifests as painful ulcers with burning sensations and inflammation in the oral cavity, sometimes associated with a metallic taste, swollen gums, and difficulty in swallowing.
Food related causes Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Excessive consumption of hot, spicy, and sour foods that increase Pitta
- Eating incompatible foods or consuming heavy, fried foods
- Frequent consumption of acidic beverages or alcohol
Behavioral Causes of Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Mental stress and anxiety
- Overexposure to the sun or heat
- Lack of oral hygiene or improper cleaning of the mouth
- Excessive physical exertion or lack of proper rest
Reference:
- Sushruta Samhita, Uttara Tantra, 53/4: "Ati ushna amla ruksha bhojanam pitta prakopam" (Consuming hot, sour, and dry foods increases Pitta, contributing to oral issues).
Pathogenesis Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
When Pitta and Kapha doshas are aggravated, they impair the natural balance of oral tissues, resulting in inflammation, ulceration, and pain in the mouth. Aggravated Pitta causes heat and burning, while Kapha contributes to mucus accumulation and heaviness in the affected area.
Reference:
- Madhava Nidan, Mukha Roga Nidan, 47/4: "Mukha roga pitta kapha dosha pradhana vikara" (Diseases of the mouth are primarily due to Pitta and Kapha imbalance).
Diagnosis Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
Ayurvedic diagnosis includes examining doshic involvement through oral inspection and pulse diagnosis. Assessment of lifestyle and dietary habits is also essential.
Reference:
- Yogaratnakara, Mukha Roga Chikitsa, 53/12: "Rasa, sparsha, nadi pariksha pitta kaphaja vyadhi nirdharana" (Diagnosis of doshic involvement in oral diseases through tongue, touch, and pulse examination).
Presymptoms of Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Mild burning and tingling in the mouth
- Sensitivity to spicy or acidic foods
- Metallic taste or bad taste in the mouth
Symptoms of Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Painful sores and ulcers in the mouth
- Burning sensation on consuming hot or spicy foods
- Swelling and redness in the oral cavity
- Foul taste or bad breath
- Difficulty in eating, chewing, and swallowing
Symptoms descriptions of Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Painful sores and ulcers in the mouth
- Burning sensation on consuming hot or spicy foods
- Swelling and redness in the oral cavity
- Foul taste or bad breath
- Difficulty in eating, chewing, and swallowing
Types of Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Pittaja Mukha Paaka: Burning ulcers with redness and inflammation.
- Kaphaja Mukha Paaka: Heavy ulcers with mucus and white coating.
- Vataja Mukha Paaka: Dry, cracked sores with sharp pain.
Complications due to Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Malnutrition due to difficulty eating
- Chronic inflammation in the mouth
- Increased susceptibility to oral infections
Curable or Non curable probability of Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
If treated early, Mukha Paaka responds well to dietary changes and herbal treatments. Chronic cases require consistent care to prevent recurrence.
Treatment of Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
-
Panchakarma (Detoxification):
- Virechana (Purgation): Helps in eliminating excess Pitta from the system.
- Gandusha (Oil Pulling): Oil gargling with coconut or sesame oil to soothe and heal the mouth.
Reference:
- Charaka Samhita, Chikitsa Sthana, 26/35: "Mukha paka virechana pitta shamaka" (Purgation therapy helps relieve Mukha Paaka by reducing Pitta).
-
Herbal Remedies:
- Stomatitis Kit
- Mamsa Pachak kwath
- Kamdudha Vati
- Suthshekhar vati
- Avipattikar churn
- Yashtimadhu (Licorice): Soothes the ulcers and reduces inflammation.
- Triphala: Acts as a mild laxative, helping in the elimination of Pitta and promoting oral health.
- Mulethi (Licorice): Reduces burning and promotes healing of ulcers.
-
Shamana Chikitsa (Pacification Therapy):
- Gargle with cool, mild decoctions of Triphala or Yashtimadhu to reduce inflammation and soothe the mouth.
- Apply Tankan Bhasma or pure Honey
- Apply Ghee (clarified butter) directly to the ulcers for healing.
Do's in Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Prefer soft, cooling, and sweet foods such as milk, rice gruel, and ghee.
- Avoid hot, spicy, and fried foods that aggravate Pitta.
- Include cooling herbs and fruits like amla, cucumber, and coconut water.
Reference:
- Charaka Samhita, Sutrasthana, 28/7: "Sheetam madhuram annam pittam shamayati" (Cooling and sweet foods pacify Pitta and are beneficial in Mukha Paaka).
Dont's in Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Avoid sour, salty, and pungent foods.
- Refrain from tobacco, alcohol, and caffeinated beverages.
- Limit stress, exposure to sunlight, and physical exertion
Modern Correlation of Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
Stomatitis is characterized by inflammation and ulceration of the mouth lining, which can result from bacterial, viral, or fungal infections or from an autoimmune response. Ayurveda views this condition as a Pitta-dominated imbalance and emphasizes treatment by pacifying Pitta and cleansing the body of toxins through dietary adjustments, herbal remedies, and lifestyle modifications.
Invistigations in Stomatitis (Mukha Paaka)
- Nadi Pariksha (Pulse Diagnosis): For assessing doshic involvement, particularly Pitta.
- Oral Examination: To observe the extent of ulcers, inflammation, and coatings.
- Blood Tests: To rule out infections and check for deficiencies, especially iron and vitamin B12.
- Biopsy: In chronic cases, a biopsy may be conducted to rule out other conditions.
Give your Feedback and Reviews
Rating Breakdown
No feedback available.